More than 90% of U.S. and European banks have explored blockchain technology. If you're like most people, you've probably heard of blockchain but don't know what it is. If you know what it is, you might not understand how it works or why it's such a big deal.
This article will break down everything you need to know about blockchain technology, from its concept to applications. We'll also discuss some of the potential implications of this new technology for businesses and individuals alike.
So, whether you're a total beginner or just looking for a refresher course, read on for an introduction to blockchain 101.
Jump to a Section
The Basic Concept
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages of development, with a limited but growing number of real-world applications. However, the potential uses for blockchain technology are far-reaching and have the potential to revolutionize a wide range of industries.
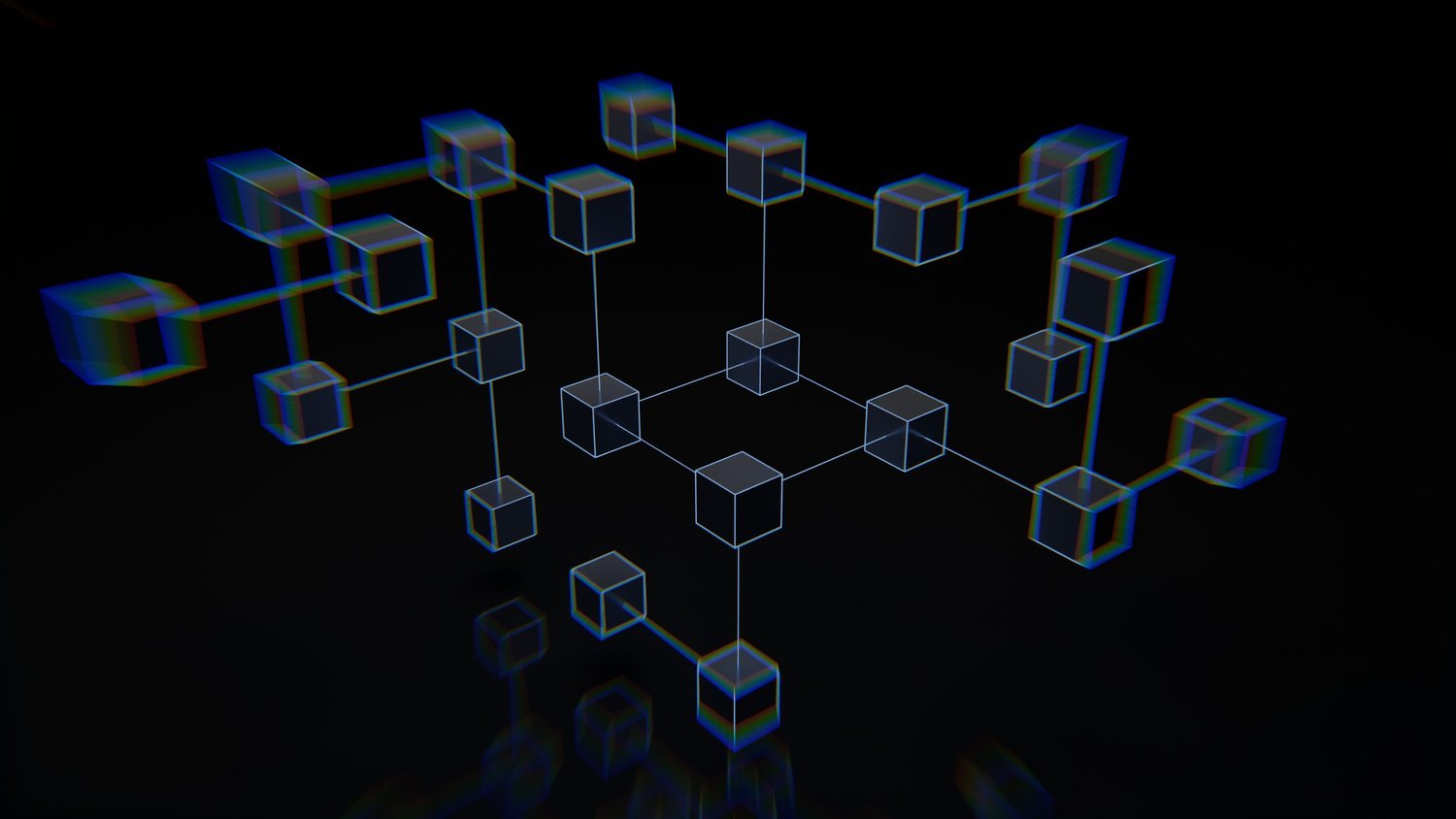
At its core, blockchain is a distributed database (sometimes referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology), that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record keeping. Blockchain records are immutable, meaning they cannot be modified or deleted once they have been added to the chain. This makes blockchain an ideal platform for storing sensitive data like financial transactions or medical records.
Blockchain technology enables new types of applications that were not previously possible. For example, blockchain can be used to develop a wide variety of decentralized applications (aka, dApps or DAPPs) that run on a peer-to-peer network. This can potentially eliminate the need for central servers and create a more efficient way of handling information and transactions.
Blockchain also has the potential to streamline supply chains and make them more transparent. By tracking goods and materials on a blockchain, businesses are able to trace the origins of their products and ensure that they are sourced from ethical and sustainable suppliers.
Blockchain technology is evolving and being refined. However, the uses for this transformative technology are vast and have the potential to change the way we live, work, and interact with the world around us.
Blockchain Prerequisites
Prerequisites to fully understand blockchain technology include a basic understanding of public-key cryptography, digital signatures, and hashing functions. In addition, some basic knowledge of game theory and distributed systems would be helpful. With these concepts in hand, one can understand how the blockchain works and why it is secure.
Public-key Cryptography
Public-key cryptography is a form of cryptography (i.e., secure communications technology) that uses two different keys, one for encryption (a way to protect/secure information) and one for decryption (a way to access secure info online with the appropriate access permissions).
The key for encryption is made public, while the key for decryption is kept private. This means that anyone can encrypt data using the public key, but only the private key holder can decrypt it.
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are a way of verifying the sender’s identity of a message or document. They work by attaching a cryptographic signature to the message or document. This signature can then be verified using the sender's public key. If the signature is valid, it proves that the message or document came from the private key owner and has not been tampered with.
Blockchain technology makes use of both public-key cryptography and digital signatures to achieve its security and decentralization goals. By understanding these two concepts, you can gain a much better understanding of how blockchain works.
What Are the Different Types of Blockchain?
This is a question often asked by those who are new to the world of blockchain technology. After all, with so many different types of blockchain platforms, it can be difficult to keep track of them all. Below, we will provide a brief overview of the most popular types of blockchain: public blockchains, permissioned blockchains, and private blockchains.
Public Blockchains
A public blockchain is a decentralized ledger that anyone can join or leave at any time. No central authority controls the network, and anyone can validate transactions or create new ones. Bitcoin is an example of a public blockchain.
Permissioned Blockchains
A permissioned blockchain is also a decentralized ledger, but there are restrictions on who can validate transactions and add new ones to the chain. Unlike public blockchains, permissioned blockchains usually have a central authority that controls access to the network. Ethereum is an example of a permissioned blockchain.
Private Blockchains
A private blockchain is a centralized ledger where only invited participants can validate transactions and add new ones to the chain. The central authority controls who has access to the network and what actions they can take. Private blockchains are used by organizations that want more control over their data and transactions.
The Importance of Blockchain
The importance of blockchain technology is often discussed in the context of cryptocurrency. However, blockchain offers numerous potential uses beyond cryptocurrency, including smart contracts, supply chain management, and more. Let's discuss the potential applications of blockchain technology and why it's essential.
Blockchain is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are built on blockchain technology, but blockchain applications extend far beyond cryptocurrency. Here are some potential uses for blockchain technology:
Supply chain management: Blockchain can be used to track the movement of goods through a supply chain. This would allow businesses to ensure that their products are coming from where they say they're coming from and that child labor or other unethical practices are not being used.
Smart contracts: A smart contract is a digital contract that can be executed automatically. For example, a smart contract could automatically buy insurance when someone buys a ticket for a flight. This would eliminate the need for paper contracts and manual processing.
Land registry: In many countries, the land registry is outdated and prone to fraud. Blockchain could be used to create a secure, transparent land registry that would make it harder for people to commit fraud.
Art registry: Art is prone to fraud, and often the original rights holders don’t get compensated for the sale of their artwork. Blockchain could be used to create a secure, transparent art registry that would make it harder for people to commit fraud.
Identity management: Blockchain could be used to create a decentralized identity management system. This would allow people to control their data and prevent identity theft.
Voting: Blockchain technology has the ability to make the voting process more easily accessible while improving security. Each vote would be attributed to one ID, and with the ability to create a fake ID being impossible, government officials could tally votes more efficiently and effectively.
These are just a few of the potential uses of blockchain technology. It's important to note that blockchain is still in its early stages, and it will take time for these applications to be fully developed and implemented. However, the potential uses for blockchain are vast.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain
The difference between Bitcoin and Blockchain is often misunderstood. To put it simply, Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency, and blockchain is the technology that underpins it. However, there is much more to each than that. Let’s take a closer look at the key differences between Bitcoin and Blockchain.
Bitcoin is a digital asset and a payment system invented by Satoshi Nakamoto. It was created as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system to enable online payments without the need for a third party such as a bank or financial institution. Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain. Bitcoin is unique in that only 21 million bitcoins will ever be created.
Blockchain is the underlying technology that enables the existence of Bitcoin, other cryptocurrencies and distributed apps. It is a distributed database that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record-keeping. While Bitcoin and Blockchain are often used interchangeably, it's essential to understand that they are not the same. Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency built on top of blockchain technology. On the other hand, Blockchain is a distributed database that can be used for a variety of applications. So, while Bitcoin uses blockchain technology, blockchain is not limited to just Bitcoin.
Bitcoin 101
In 2009, an anonymous person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto launched Bitcoin, the world’s first cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual tokens that use cryptography to secure their transactions and control the creation of new units. Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency and remains the best known. There are now more than 1,600 cryptocurrencies in existence!
Bitcoin is often referred to as a digital or virtual currency, but it is actually a type of electronic money. It shares many attributes with traditional ‘fiat’ currencies (such as the U.S. dollar) but also has some unique characteristics that set it apart. One key difference is that bitcoins are decentralized. Unlike traditional currencies, which central banks issue, Bitcoin has no central monetary authority.
The Bitcoin network is designed to produce a finite supply of 21 million bitcoins. This number will never change, and it is programmed into the Bitcoin software. As more people start using Bitcoin, the demand for bitcoins increases, and the price goes up.
How does a Bitcoin transaction work?
When someone sends you bitcoins, they essentially sign off ownership of the coins to your crypto wallet's address. To do this, they use the private key associated with their wallet. Once your wallet receives a signed transaction from the sender, it uses your private key to verify that it is a valid transaction. If everything checks out, the transaction is then broadcast to the Bitcoin network so that blockchain ‘miners’ can verify the transaction and include it in the next block of the blockchain and confirm it. Once blockchain miners confirm a transaction, it is added to the blockchain and is considered permanent. This process of verifying transactions on a blockchain is known as "mining."
What is Bitcoin mining?
Bitcoin mining is how new bitcoins are created. Miners are rewarded with bitcoins for verifying and committing transactions to the blockchain. Mining requires special hardware and consumes a lot of electricity. It is also a competitive process, where miners race to solve math problems with their computers to verify transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. The first miner to verify a transaction is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins as an incentive.
The Blockchain: In Blocks We Trust
The blockchain is a distributed digital ledger that records all cryptocurrency transactions. It is constantly growing as "completed" blocks are added with a new set of recordings. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
A blockchain consists of three types of elements: blocks, transactions, and nodes. A block stores information about cryptocurrency transactions. Transactions are combined into a block after nodes verify them through cryptographic hashing. Nodes are computers that store a complete copy of the blockchain and work together to verify and approve new blocks.
When a transaction is made, it is broadcast to all nodes on the network. Nodes then use cryptography to verify the digital signature of the transaction and whether it has been tampered with. Once verified, the transaction is combined into a block with other verified transactions. This block is then added to the blockchain.
Blocks are added to the blockchain in a linear, chronological order. Each new block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block with a timestamp and transaction data. This ensures that no one can go back and modify past blocks, as that would change the cryptographic hash of the blocks that come after it.
“Proof-Of-Work” Consensus Mechanism
The “proof-of-work” (POW) consensus mechanism is a system that is used to verify and validate transactions on a blockchain network. It is also used to prevent double-spending of digital assets. The POW consensus mechanism works by requiring nodes, or network members (aka miners), to solve complex mathematical problems to verify each transaction. The first node to solve the problem gets to add the following block of transactions to the blockchain. This process is known as “mining.” The POW consensus mechanism is used by most public blockchain networks, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum.
The main benefit of the POW consensus mechanism is that it is a very secure way to verify and validate transactions on a blockchain network. This is because it is very difficult for attackers to control more than 50% of the computing power on the network (known as a “51% attack”). Additionally, the POW consensus mechanism incentivizes people to participate in mining activities, as they can earn rewards for doing so.
No Supreme Leaders
Decentralization refers to the distribution of power or responsibility away from a central authority. When applied to technology, decentralization typically refers to the creation of distributed networks where each node in the network can independently verify transactions and contribute to the ledger without the need for centralized intermediaries.
The decentralization of the blockchain means that no single entity has control over the network. This allows for a more secure and transparent ecosystem where users can transact without the need to trust a third party.
There are many advantages of a decentralized blockchain, including:
Security: With no central point of control, decentralization makes it much more difficult for hackers to target the network.
Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are recorded on a public ledger, which anyone can access. This increases transparency and accountability.
Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This ensures that data is tamper-proof and cannot be corrupted.
Scalability: The decentralized nature of the blockchain means that it can be scaled to accommodate a large number of users and transactions.
Efficiency: Decentralization can help to reduce costs and increase efficiency by eliminating the need for mediators and intermediaries.
Blockchain-Based Services
With the advent of blockchain technology, a whole new world of possibilities has opened up in business and commerce. Blockchain-based services offer many advantages and benefits that traditional centralized services cannot match.
Here is a list of some of the most popular and useful blockchain-based services currently available:
Decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges: Decentralized exchanges are cryptocurrency exchanges that are not centrally controlled or managed by any single entity. This means that there is no central point of failure or control, and users have full control over their own funds. Decentralized exchanges are often seen as more secure and resilient than traditional centralized exchanges, as they are much less susceptible to hacks and security breaches.
Decentralized storage: Decentralized storage platforms offer a secure and resilient way to store data without the need for a central server or authority. Data is instead stored on a network of distributed nodes, which makes it much more difficult for hackers to target and corrupt.
Blockchain-based identity management: Identity management systems based on blockchain technology provide a secure and tamper-proof way to store and manage digital identities. This can be used for everything from online security and authentication to proving ownership of digital assets such as domain names or copyrighted content.
Real Estate: The average homeowner sells his or her home every five to seven years, and the average person will move nearly 12 times during their lifetime. Blockchain can help expedite home sales by quickly verifying finances, reducing fraud thanks to its encryption, and offering transparency throughout the entire selling and purchasing process.
Blockchain-based voting: Blockchain-based voting systems offer the potential for a more secure, transparent, and tamper-proof way to conduct elections and other types of voting. This could potentially be used to help combat voter fraud and ensure that everyone's vote is counted accurately.
Decentralized applications (DApps): DApps are applications that run on a decentralized network, such as a blockchain. They are often open source and can be used for everything from social networking and messaging to gaming and financial services.
Initial coin offerings (ICOs): ICOs are a type of crowdfunding campaign that uses cryptocurrency tokens instead of traditional fiat currency (such as US dollars). They are often used to raise funds for new blockchain-based projects and businesses.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): A DAO is a digital organization that is run by a set of rules encoded on a blockchain. They are decentralized and autonomous, meaning that they are not controlled by any central authority.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
The growing popularity of blockchain technology has led many industries to investigate how the distributed ledger system can be used to streamline their processes. However, as with any new technology, there are also a number of potential disadvantages of implementing a blockchain system.
One of the main disadvantages of blockchain is that it is immutable; once data is written to the blockchain it cannot be changed or deleted. While this is beneficial in terms of ensuring data integrity, it also means that any errors made in the data entry process cannot be corrected. This could lead to problems if inaccurate information is recorded on the blockchain.
Another disadvantage of blockchain is that it is often slow and cumbersome compared to traditional database systems. This is due to the fact that each block in the chain must be verified and confirmed by all the nodes in the network before it can be added, which can take some time.
Blockchain systems are also often quite complex and can be difficult to understand and use. This can make them less user-friendly than more traditional database systems and can limit their adoption.
Finally, blockchain technology is still in its infancy and has not yet been fully tested over time. This means that there is a potential for unforeseen problems to arise when it is implemented on a large scale over time.
What Lies Ahead
The future of blockchain is exciting. With the advent of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with the digital world. Here are three ways that blockchain could change the internet as we know it:
Decentralized Applications (dApps)
There is no need for a centralized authority to manage and control digital applications with blockchain. This means that anyone can create and deploy a dApp without going through a third-party platform such as Apple’s App Store or Google Play.
This also makes it possible for developers to create dApps that are not controlled by any single entity. This could potentially lead to the development of more innovative and user-friendly applications that are not subject to the whims of a central authority.
Distributed Storage
Another way that blockchain could change the internet is by developing distributed storage solutions. With traditional storage solutions, data is stored on central servers that are owned and operated by a single company.
If those servers are hacked or experience downtime, users can lose access to their data. However, with a distributed storage solution powered by blockchain, data would be spread across multiple nodes on a network.
This would make it much more difficult for hackers to target and would also make the system more resilient to outages.
Enhanced Security
One of the most important advantages of blockchain technology is its enhanced security. With traditional systems, data is often stored in a central location where hackers can more easily target it.
However, with blockchain, data is distributed across a network of nodes. This makes it much more difficult for hackers to access sensitive data. In addition, the use of cryptographic techniques can further secure data and make it tamper-proof.
As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and solutions that will make our lives easier and more efficient.
How Can EquityBrix Help?
EquityBrix can help you grow your wealth through our fractional real estate investment, blockchain-integrated platform. Our team marries the needs of investors and real estate developers by providing opportunities for above-market returns. EquityBrix is committed to creating high-yield investment offerings, and we can help guide you through the new era of real estate investing.
If you want more information about tokenized real estate investing go to EquityBrix or EquityBrix.com/Learn.
If you are looking to grow your wealth and diversify your investment portfolio by learning about innovative ways of investing in real estate go to EquityBrix, or contact us for more information, or sign-up for the EquityBrix Newsletter.
*Disclaimer: EquityBrix is not an investment adviser. This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute investment or tax advice. It’s important to be informed and to make your own investment decisions or do so in consultation with a professional financial advisor. Under no circumstances should this material be used or considered as an offer to sell or a solicitation of any offer to buy an interest in any investment. Any such offer or solicitation will be made only by means of a written online prospectus relating to the particular investment.